| |
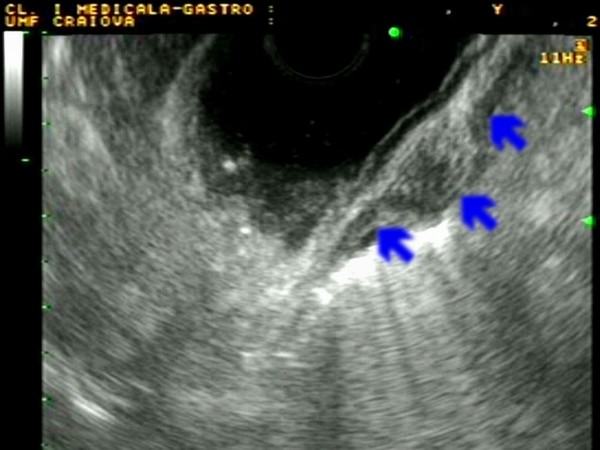
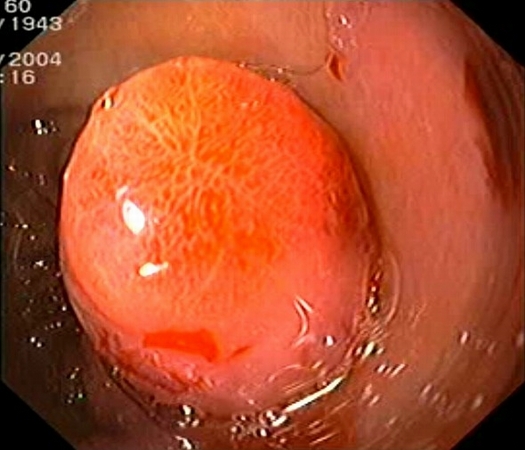
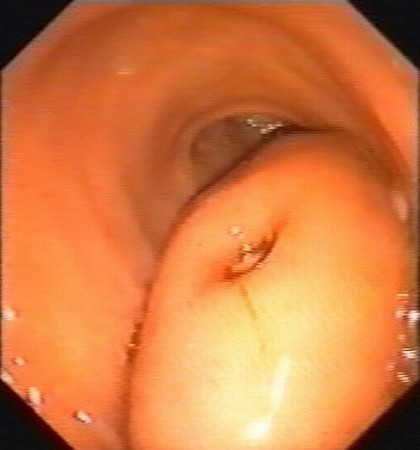
| Patient with a 1.5 cm gastric submucosal tumor (GIST) located on above the gastric angle, with hyperemic covering mucosa. EUS identified an homogenous tumor originating in the 3rd EUS layer (submucosa), with intact muscularis propria (blue arrows), ensuring safe endoscopic submucosal resection (ESMR). Complete ESMR by the cap aspiration method was subsequently performed (see also Interventional EUS). Pathology confirmed a benign GIST, completely resected (c-kit+, actin-, S-100-). |
 |
 |
| |
More images / movies:



|
|
|
| |
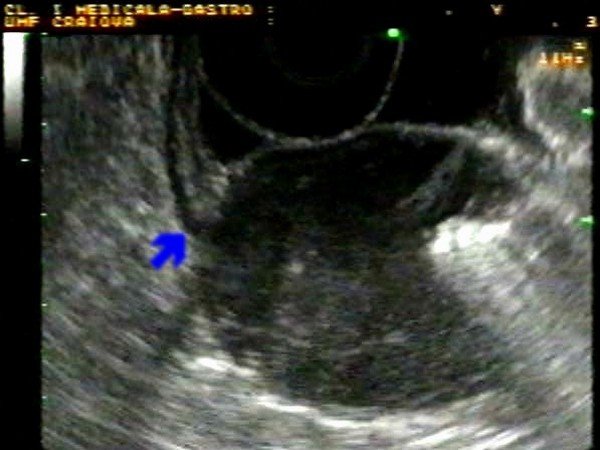
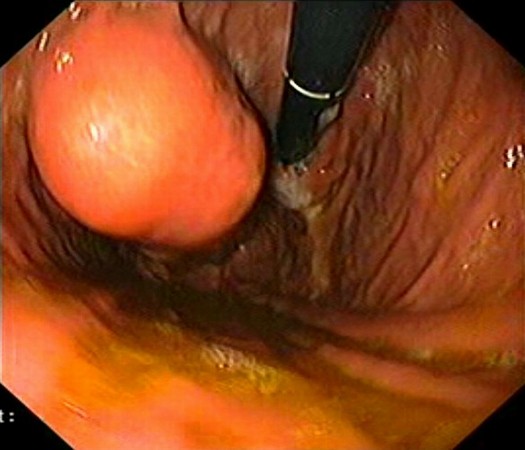
| Patient with a submucosal tumor located in the posterior face of the gastric antrum, with normal covering mucosa. EUS identified a 4.5 cm tumor originating in the 4th layer (blue arrow) of the gastric wall (muscularis propria), with air inside the central ulceration visualized during endoscopy. Due to the strong suspicion of a GIST tumor, the patient was referred to surgery, while pathology confirmed a benign GIST tumor (c-kit+, CD34+, actin+, S-100-). |
 |
 |
| |
|
|
|
| |
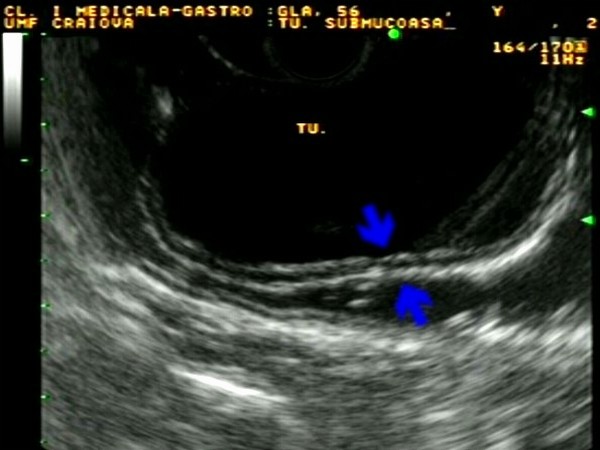
| Patient with a submucosal tumor located on the anterior wall, 5 cm below the gastroesophageal junction, with normal covering mucosa. EUS identified the tumor as originating from the muscularis propria, with normal mucosa and submucosa covering the tumor (blue arrows). EUS-FNA was performed but it did not yielded sufficient material for pathology. Subsequently, the patient was referred for surgery, which confirmed a benign GIST. |
 |
 |
| |
|
|
|
| Malignant GIST |
Jan 23, 2005 |
|
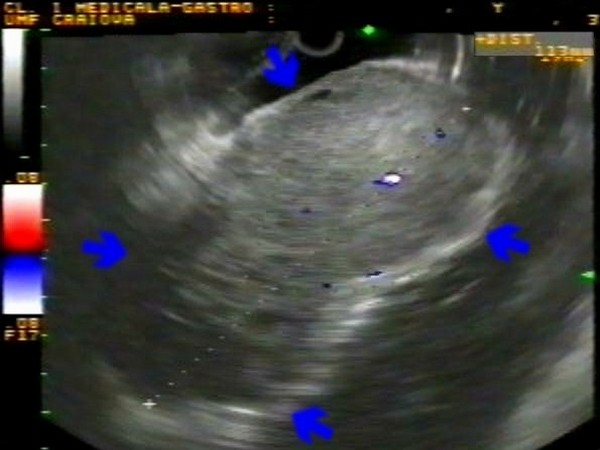
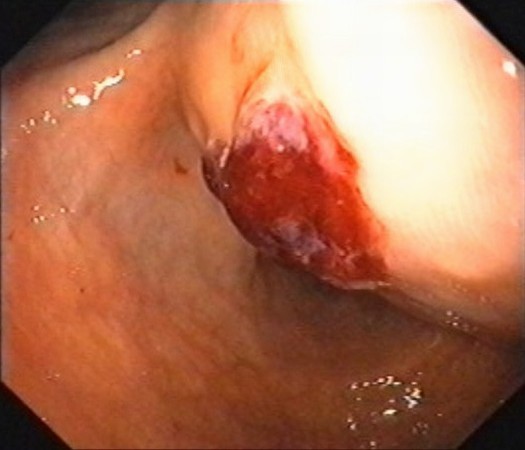
| Patient with a recent episode of upper gastrointestinal bleeding with a large (12 cm) gastric submucosal tumor located on the anterior wall towards the lesser curve, with normal covering mucosa and a central ulceration with diffuse bleeding. EUS identified an inhomogenous tumor, with hypo- and hyperechoic areas, and vascular signals in color Doppler mode. |
 |
 |
| |
|
|
|
|




